Neutron Thermalization Studies in Graphite
Nuclear Science and Engineering / Volume 22 / Number 1 / May 1965 / Pages 40-50
Technical Paper / dx.doi.org/10.13182/NSE65-A19761
Articles are hosted by Taylor and Francis Online.
The neutron diffusion and integral scattering properties of graphite have been measured by the pulsed-neutron-source technique. Measurements were performed on assemblies with geometric bucklings from 0.0036 to 0.0151 cm−2. The time of attainment of asymptotic neutron-energy spectra was determined from transmission measurements. Results from these latter measurements indicated that the minimum thermalization time, for the assemblies investigated, was ≈ 2 msec. Asymptotic ‘average’ neutron velocities, measured both internally and externally, were obtained as a function of assembly size. Results indicated that an asymptotic neutron spectrum did not exist for assemblies with B2 ≈ 0.015 cm−2 at a time 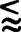 2 msec after the neutron pulse. A value of the diffusion cooling coefficient, C = 45.6 ± 4.7 × 105 cm4/sec was derived from the measured ‘thermal’ neutron decay constants.
2 msec after the neutron pulse. A value of the diffusion cooling coefficient, C = 45.6 ± 4.7 × 105 cm4/sec was derived from the measured ‘thermal’ neutron decay constants.


