An Anisotropic Neutron Collimating System for Proton Accelerator–Generated Secondary Particles
Nuclear Technology / Volume 211 / Number 11 / November 2025 / Pages 2870-2879
Articles are hosted by Taylor and Francis Online.
Proton–stainless steel interactions occurring at the first collimator of the Middle East Technical University Defocusing Beamline generate high-energy secondary particles like neutrons (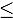 23 MeV), gamma rays (
23 MeV), gamma rays (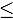 14 MeV), and electrons and positrons (
14 MeV), and electrons and positrons (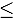 7.0 MeV) with particle fluxes between 107 to 109 particles/(cm2∙s). A neutron collimating system aiming to reduce most of these secondaries and obtain a moderate flux of fast neutrons was designed and constructed. The collimating structure consists of a moderating unit aiming to shield the outside of the system, a neutron funnel to redirect the neutrons to the desired beam geometry, and a testing station. This system funnels neutrons into a 10-cm-diameter nonuniform beam and directs them to a testing area capable of hosting up to six samples of 7.3-cm diameter and up to 3.0-cm thickness. Simulation results show neutrons with energies up to 5.0 MeV and a flux of 106 neutrons/(cm2∙s) at the testing unit, while the experimental result gives a neutron dose rate of about 22 mSv/h.
7.0 MeV) with particle fluxes between 107 to 109 particles/(cm2∙s). A neutron collimating system aiming to reduce most of these secondaries and obtain a moderate flux of fast neutrons was designed and constructed. The collimating structure consists of a moderating unit aiming to shield the outside of the system, a neutron funnel to redirect the neutrons to the desired beam geometry, and a testing station. This system funnels neutrons into a 10-cm-diameter nonuniform beam and directs them to a testing area capable of hosting up to six samples of 7.3-cm diameter and up to 3.0-cm thickness. Simulation results show neutrons with energies up to 5.0 MeV and a flux of 106 neutrons/(cm2∙s) at the testing unit, while the experimental result gives a neutron dose rate of about 22 mSv/h.


