
Home / Publications / Journals / Nuclear Technology / Volume 70 / Number 2
Measurement of the Iodine Partition Coefficient
Nuclear Technology / Volume 70 / Number 2 / August 1985 / Pages 290-293
Technical Note / Nuclear Safety / dx.doi.org/10.13182/NT85-A33655
Articles are hosted by Taylor and Francis Online.
The overall partition coefficient P describes the distribution of iodine between the iodine in bulk aqueous solution and in the vapor phase: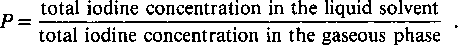 The hydrolysis of iodine is complicated because it involves a number of species that differ considerably in their individual volatilities. Large uncertainties exist in the thermodynamic data of some of the iodine species, especially at temperatures above 25 °C. Because of this, an experiment was undertaken to measure the partition coefficient under varying physical and chemical conditions. Measurements of P were made for a temperature range of 21 to 113 °C under well-defined conditions (liquid molar concentration, pH, and redox potential) for inorganic iodine. The experimental results are interpreted with the aid of an analytical model and published thermodynamic data. A good agreement between calculated and measured values was found. The experimental setup allows the determination of very high partition coefficients up to a value of 2.0 × 106. This is demonstrated by adding cesium-iodide to the fuel pool water of a boiling water reactor.
The hydrolysis of iodine is complicated because it involves a number of species that differ considerably in their individual volatilities. Large uncertainties exist in the thermodynamic data of some of the iodine species, especially at temperatures above 25 °C. Because of this, an experiment was undertaken to measure the partition coefficient under varying physical and chemical conditions. Measurements of P were made for a temperature range of 21 to 113 °C under well-defined conditions (liquid molar concentration, pH, and redox potential) for inorganic iodine. The experimental results are interpreted with the aid of an analytical model and published thermodynamic data. A good agreement between calculated and measured values was found. The experimental setup allows the determination of very high partition coefficients up to a value of 2.0 × 106. This is demonstrated by adding cesium-iodide to the fuel pool water of a boiling water reactor.

