A Robust, Relaxation-Free Multiphysics Iteration Scheme for CMFD-Accelerated Neutron Transport k-Eigenvalue Calculations—II: Numerical Results
Nuclear Science and Engineering / Volume 195 / Number 11 / November 2021 / Pages 1202-1235
Technical Paper / dx.doi.org/10.1080/00295639.2021.1906586
Articles are hosted by Taylor and Francis Online.
In a companion paper, we present the theoretical development of a new robust, relaxation-free iteration scheme for multiphysics 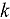 -eigenvalue problems. These types of problems are essential to the study of computational reactor physics and in particular whole-core, high-fidelity simulation codes. The deterministic whole-core simulation tools invariably rely on the coarse mesh finite difference (CMFD) acceleration for fast convergence. However, the use of CMFD-accelerated transport in multiphysics problems coupled via Picard iteration is not robust and is frequently treated with relaxation. In this paper, we build on our previous theoretical work that uses Fourier analysis to prove how stability and efficient convergence can be achieved in the multiphysics problem by appropriately loosening the convergence criteria of the low-order diffusion acceleration equations. Specifically, we develop a methodology for estimating a key problem-dependent parameter, the feedback intensity, required by the nearly optimally partially converged coarse mesh finite difference (NOPC-CMFD) method. We then describe the implementation of NOPC-CMFD in the Michigan Parallel Characteristics Transport (MPACT) code and perform several numerical calculations. Problems ranging from a single pressurized water reactor (PWR) fuel rod to a full-core PWR cycle depletion are analyzed to assess the performance and robustness of NOPC-CMFD over a wide range of conditions that consider multiple forms of multiphysics feedback. The results verify the theoretical predictions of our companion paper, illustrating that the NOPC-CMFD is superior to current CMFD or nonlinear diffusion acceleration schemes that use relaxation. Overall, the method is able to recover the performance of traditional CMFD in problems without feedback for a wide range of conditions. This was observed to result in a substantial reduction, up to 40%, of the run time in whole-core cycle depletion problems.
-eigenvalue problems. These types of problems are essential to the study of computational reactor physics and in particular whole-core, high-fidelity simulation codes. The deterministic whole-core simulation tools invariably rely on the coarse mesh finite difference (CMFD) acceleration for fast convergence. However, the use of CMFD-accelerated transport in multiphysics problems coupled via Picard iteration is not robust and is frequently treated with relaxation. In this paper, we build on our previous theoretical work that uses Fourier analysis to prove how stability and efficient convergence can be achieved in the multiphysics problem by appropriately loosening the convergence criteria of the low-order diffusion acceleration equations. Specifically, we develop a methodology for estimating a key problem-dependent parameter, the feedback intensity, required by the nearly optimally partially converged coarse mesh finite difference (NOPC-CMFD) method. We then describe the implementation of NOPC-CMFD in the Michigan Parallel Characteristics Transport (MPACT) code and perform several numerical calculations. Problems ranging from a single pressurized water reactor (PWR) fuel rod to a full-core PWR cycle depletion are analyzed to assess the performance and robustness of NOPC-CMFD over a wide range of conditions that consider multiple forms of multiphysics feedback. The results verify the theoretical predictions of our companion paper, illustrating that the NOPC-CMFD is superior to current CMFD or nonlinear diffusion acceleration schemes that use relaxation. Overall, the method is able to recover the performance of traditional CMFD in problems without feedback for a wide range of conditions. This was observed to result in a substantial reduction, up to 40%, of the run time in whole-core cycle depletion problems.


