An Instrument for Nondestructively Testing Fuel Core to Cladding Heat Transfer
Nuclear Science and Engineering / Volume 12 / Number 2 / February 1962 / Pages 271-275
Technical Paper / dx.doi.org/10.13182/NSE62-A26067
Articles are hosted by Taylor and Francis Online.
An instrument for nondestructively mapping core to cladding heat transfer quality in nuclear fuel elements has been developed. Heat transfer defects down to 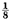 in. diameter in Zircaloy-2 clad and down to
in. diameter in Zircaloy-2 clad and down to 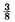 in. diameter in X-8001 aluminum alloy clad uranium fuel elements have been detected. An infrared radiometer was used to detect fuel element surface temperature variations during induction or plasma arc jet heating. The unusual application of plasma arc heating in this instrument made heat transfer testing of nonuniform fuel elements feasible.
in. diameter in X-8001 aluminum alloy clad uranium fuel elements have been detected. An infrared radiometer was used to detect fuel element surface temperature variations during induction or plasma arc jet heating. The unusual application of plasma arc heating in this instrument made heat transfer testing of nonuniform fuel elements feasible.


