Reich-Moore Parameterization of (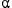 ,n) Reactions on Light Nuclei: Impact on a Neutron Source Calculation in an Oxide Fuel
,n) Reactions on Light Nuclei: Impact on a Neutron Source Calculation in an Oxide Fuel
Nuclear Science and Engineering / Volume 151 / Number 2 / October 2005 / Pages 135-156
Technical Paper / dx.doi.org/10.13182/NSE05-A2536
Articles are hosted by Taylor and Francis Online.
Evaluated data are adjusted on experimental measurements using nuclear reaction models. Among these data, those concerning alpha-particle interactions on light nuclei are not well known, although crucial for neutron emission problems via (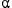 ,n) processes in nuclear fuels (oxide, carbide, nitride). Examples of applications are reprocessing, packaging and storage of radioactive waste, and intrinsic neutron source term evaluation in critical and subcritical reactors (accelerator-driven systems). The goal is the modeling of (
,n) processes in nuclear fuels (oxide, carbide, nitride). Examples of applications are reprocessing, packaging and storage of radioactive waste, and intrinsic neutron source term evaluation in critical and subcritical reactors (accelerator-driven systems). The goal is the modeling of (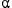 ,n) reactions on oxygen isotopes to extract the resonance parameters. The SAMMY code, which relies on the Reich-Moore approximation of the R-matrix theory, is used. In the most recent version, the SAMMY code allows the study of the in- and outgoing charged-particle channels. An important validation of this new feature has been made. In addition, a manifest lack of experimental data for this type of reaction has been underlined. Finally, the impact of the new pointwise description of the (
,n) reactions on oxygen isotopes to extract the resonance parameters. The SAMMY code, which relies on the Reich-Moore approximation of the R-matrix theory, is used. In the most recent version, the SAMMY code allows the study of the in- and outgoing charged-particle channels. An important validation of this new feature has been made. In addition, a manifest lack of experimental data for this type of reaction has been underlined. Finally, the impact of the new pointwise description of the (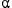 ,n) reaction cross section on the energy distribution calculation of the intrinsic neutron source of an irradiated mixed-oxide fuel pin is shown and compared to the standard calculation, which uses average cross sections.
,n) reaction cross section on the energy distribution calculation of the intrinsic neutron source of an irradiated mixed-oxide fuel pin is shown and compared to the standard calculation, which uses average cross sections.


