Thermal-Neutron Diffusion in Light and Heavy Water
Nuclear Science and Engineering / Volume 33 / Number 2 / August 1968 / Pages 209-217
Technical Paper / dx.doi.org/10.13182/NSE68-A20658
Articles are hosted by Taylor and Francis Online.
Thermal-neutron diffusion coefficients for H2O and D2O were determined from static measurements of the neutron relaxation length in boron poisoned H2O and D2O and pulsed measurements of the neutron die-away in different sized containers of these two moderators. The coefficients derived for H2O are: 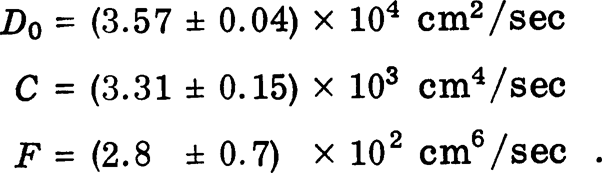 These results agree well with previously reported coefficients, fairly well with Honeck's calculations, and very well with Dorning's more recent calculations. The diffusion coefficients for D2O were derived from data in the range of (equivalent) poison concentrations, ∑a(B) = −0.04 to +0.04/cm. Restricting the data to these limits avoids possible difficulties associated with the approach to the Corngold limits at κ = (∑t)min and
These results agree well with previously reported coefficients, fairly well with Honeck's calculations, and very well with Dorning's more recent calculations. The diffusion coefficients for D2O were derived from data in the range of (equivalent) poison concentrations, ∑a(B) = −0.04 to +0.04/cm. Restricting the data to these limits avoids possible difficulties associated with the approach to the Corngold limits at κ = (∑t)min and 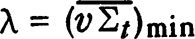 . The coefficients derived for D2O are:
. The coefficients derived for D2O are: 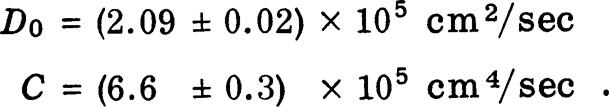 Unlike previous experiments, these results indicate no discrepancy between pulsed and static determinations of D0 for D2O.
Unlike previous experiments, these results indicate no discrepancy between pulsed and static determinations of D0 for D2O.


