Thermal-Neutron Transmission Through Plane Cadmium Covers
Nuclear Science and Engineering / Volume 20 / Number 3 / November 1964 / Pages 314-317
Technical Paper / dx.doi.org/10.13182/NSE64-A19575
Articles are hosted by Taylor and Francis Online.
The transmission of thermal neutrons through cadmium covers as a function of cadmium thickness was measured in a graphite stack at various heights above the thermal column of the AE-6 water-boiler reactor. Both dysprosium-alloy and indium-alloy foils were used as detectors and were beta-counted. Because the thermal flux incident on a cadmium cover is depressed relative to the flux incident on a bare foil, a foil with a thick cadmium cover on one side only was used for the zero-thickness measurement and its activity was doubled. The resultant thermal activities for a thin detector were consistent with the exponential integral 0.930 Ε2(dΣα) a cadmium thickness greater than 0.025 cm, where 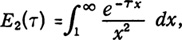 and a value of 2450 barns was used for the absorption cross section of cadmium.
and a value of 2450 barns was used for the absorption cross section of cadmium.


