Feasibility Studies of Alpha-Particle Channeling in Mirror Machines
Fusion Science and Technology / Volume 57 / Number 4 / May 2010 / Pages 361-368
Technical Note / dx.doi.org/10.13182/FST10-A9498
Articles are hosted by Taylor and Francis Online.
The linear magnetic trap is an attractive concept both for fusion reactors and for other plasma applications because of its relative engineering simplicity and high-beta operation. Applying the 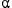 -channeling technique to linear traps such as mirror machines can benefit this concept by efficiently redirecting
-channeling technique to linear traps such as mirror machines can benefit this concept by efficiently redirecting 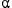 -particle energy to fuel ion heating or by otherwise sustaining plasma confinement, thus increasing the effective fusion reactivity. To identify waves suitable for
-particle energy to fuel ion heating or by otherwise sustaining plasma confinement, thus increasing the effective fusion reactivity. To identify waves suitable for 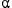 channeling, a rough optimization of the energy extraction rate with respect to the wave parameters is performed. After the optimal regime is identified, a systematic search for modes with similar parameters in mirror plasmas is performed, assuming quasi-longitudinal or quasi-transverse wave propagation. Several modes suitable for
channeling, a rough optimization of the energy extraction rate with respect to the wave parameters is performed. After the optimal regime is identified, a systematic search for modes with similar parameters in mirror plasmas is performed, assuming quasi-longitudinal or quasi-transverse wave propagation. Several modes suitable for 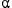 -particle energy extraction are identified for both reactor designs and for proof-of-principle experiments.
-particle energy extraction are identified for both reactor designs and for proof-of-principle experiments.


